INGOLSTADT: Audi is expanding its engine lineup for the Q5 and A6 with a three-litre V6 diesel engine delivering 220kW (299PS) and 580Nm of torque.
For the first time, the MHEV (mild hybrid electric vehicle) plus technology, which delivers up to 18kW (24PS) of additional power, is being used in combination with an electrically powered compressor.
The V6 TDI quattro can now be ordered for both models.
With MHEV plus technology, Audi offers partial electrification that enhances both performance and driving experience while reducing CO2 emissions and fuel consumption.
The foundation of this system consists of the powertrain generator, belt alternator starter, and lithium iron phosphate battery.
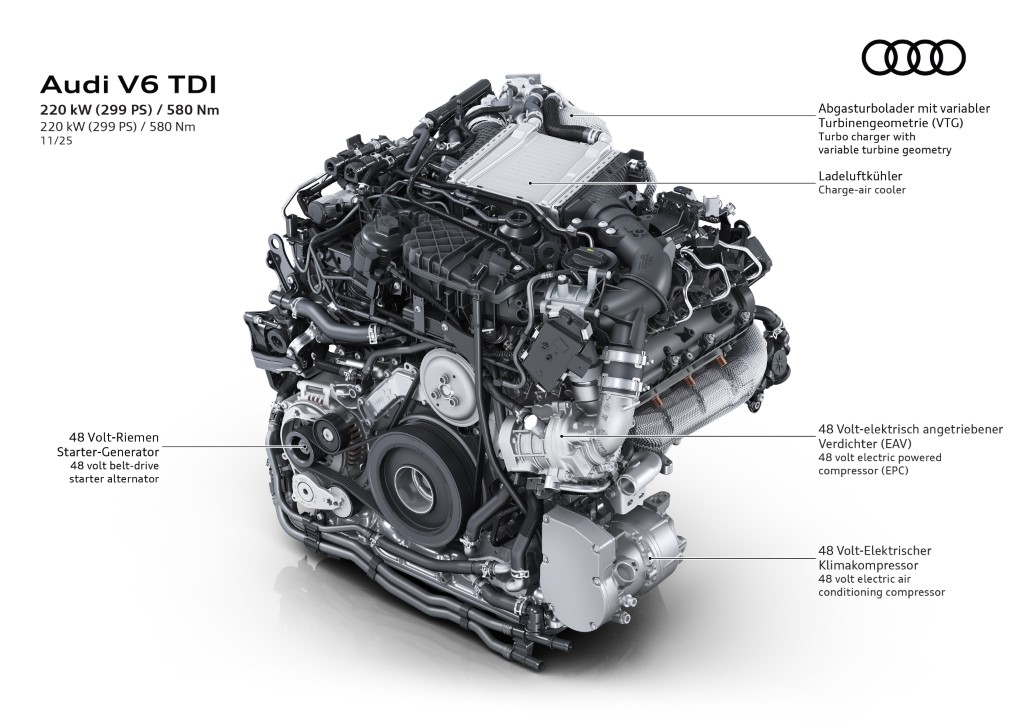
The belt alternator starter’s primary function is to start the engine and supply the battery with electrical energy.
The powertrain generator enables partially electric driving, which means that in slow city traffic, when parking and manoeuvring, and in steadily moving traffic on roads outside of towns, the vehicle operates purely electrically.
The powertrain generator also provides an additional 230Nm of drive torque and up to 18kW (24PS) of power when starting off and overtaking.
When decelerating, it feeds up to 25kW of energy back into the battery.
The electrically powered compressor is located behind the conventional turbocharger and the intercooler in the intake path.
It is powered by the 48-volt onboard electrical system.
When the load demand from the accelerator pedal is high, and the energy supply on the turbine side is low, the intake air is directed to the electrically powered compressor.
There, this air – already compressed by the exhaust-driven turbocharger – is further compressed before entering the combustion chamber.
Compared to earlier models equipped with an electrically powered compressor, such as the S4, S6, and SQ5, the current generation is significantly more powerful – thanks to a wider operating range and faster buildup of boost.
This is made possible by the optimised airflow design of the compressor and the permanent-magnet synchronous motor that drives it, in combination with improved air supply to the six cylinders.
The new V6 TDI is approved to use HVO fuel conforming to European standard EN 15940 – indicated by the XTL sticker in the fuel tank cap. XTL (X-to-liquid) is a collective term for fuels of this standard, with the “X” representing a variable source component.
HVO stands for hydrotreated vegetable oil.
This sustainable fuel enables a 70 to 95 percent reduction in CO2 emissions compared to petroleum-derived diesel.
HVO is produced using residual and waste materials, such as used cooking oil from the food industry or agricultural by-products.
Using hydrogen, the oils are converted into saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
This modifies the properties of the vegetable oils to make them suitable for use in diesel engines.
They can be blended with conventional diesel to replace fossil components or used as a 100 percent pure fuel.
New vehicles leaving the two German Audi plants in Ingolstadt and Neckarsulm are delivered with HVO fuel already in the tank.












